
After determining the unknown displacements, the other forces are calculated satisfying the compatibility conditions and force-displacement relations. Primary unknowns are the displacements and initially, force-displacement relations are computed and subsequently, equations are written satisfying the equilibrium conditions of the structure in this method.

Once the redundant forces are calculated, the remaining reactions are evaluated by equations of equilibrium. The basic methods of structural analysis applicable to framed structures are the. A B 100 kN C 4 m 4 m 8 m y B 0.04 m E 200 GPa I 500 x 10 6 mm 4 Solution: n r 3m 4 3(1) 1 Beam is indeterminate to first degree. N/B: In practical construction, it is not advisable to hinge the structure at the apex. EV302 - Structural Analysis FLEXIBILITY METHOD 11 Beam Analysis Example Textbook Example 10-3 Prepared by: Dr. The frame is hinged at point D, and it is desired to obtain the internal forces (bending moment, axial forces, and shear forces) due to the externally applied load.
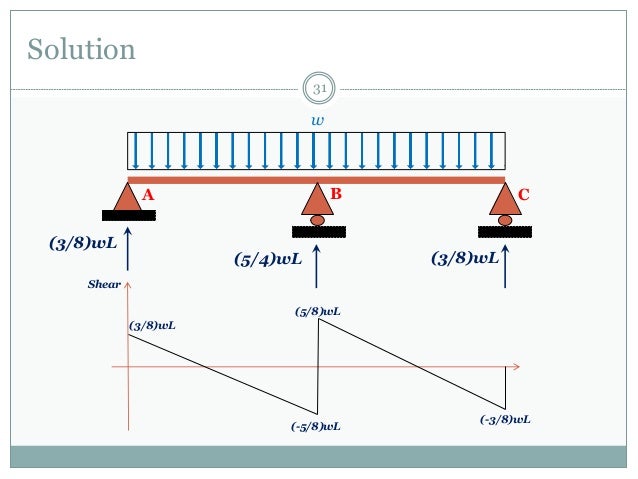
Solving these equations, redundant forces are calculated. In this post, a gable industrial frame structure is subjected to a load regime as shown below. The primary unknown forces in the members and compatibility equations are written for displacement and rotations (which are calculated by force-displacement equations) in this method.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
